Mole Concept(Numericals also)😊
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps
Term mole was suggested by Ostwald (Latin word mole = heap)
A mole is defined as the amount of substance which contains same number of elementary particles (atoms, molecules or ions) as the number of atoms present in 12 g of carbon (C-12).
1 mol = 6.023 * 1023 atoms = one gram-atom = gram atomic mass
1 mol = 6.023 * 1023 molecules = gram molecular mass
In gaseous state at STP (T = 273 K, p = 1 atm)
Gram molecular mass = 1 mol
= 22.4 L = 6.022 * 1023 molecules
Standard number 6.023x 1023 is called Avogadro number in honour of Avogadro (he did not give this number) and is denoted by NA.
The volume occupied by one mole molecules of a gaseous substance is called molar volume or gram molecular volume.
Number of moles = amount of substance (in gram) / molar mass

Number of molecule = number of moles * NA
Number of molecules in Ig compound = NA / g-molar mass
Number of molecules in 1 cm3 (1 mL) of an ideal gas at STP is called Loschmidt number (2.69x 1019).
[One amu or u (unified mass) is equal to exactly the 1 / 12th of the mass of 12C atom, i.e., 1 amu or u = 1 / 12 * mass of one carbon (C12) atom
1 amu = 1 / NA
= 1 Dalton = 1.66x 10-24 g
One mole of electrons weighs 0.55 mg (5.5x 10-4 g).
Atomic Mass
It is the average relative atomic mass of an atom. It indicates that how many times an atom of that element is heavier as compared with 1 / 12 of the mass of an atom of carbon-12.
Average atomic mass = average mass of an atom / 1 / 12 * mass of an atom of C12
The word average has been used in the above definition and is very significant because elements occur in nature as mixture of several isotopes. So. atomic mass can be computed as
Average atomic mass
= RA(1) * at. mass(1) + RA(2) * at. mass (2) / RA(l) + RA(2)
Here, RA is relative abundance of different isotopes.
In case of volatile chlorides. the atomic weight is calculated as
At. wt. = Eq. wt. x valency
and valency = 2 * vapour density of chloride / eq. wt. of metal + 35.5
According to Dulong and Petit’s rule,
Atomic weight * specific heat = 6.4
Gram Atomic Mass (GAM)
Atomic mass of an element expressed in gram is called its gram atomic mass or gram-atom or mole-atom.
Molecular Mass
It is the mass of a molecule, i.e., number of times a molecule is heavier than 1 / 12 th mass of C-12 atom. Molecular mass of a substance is an additive property and can be calculated by taking algebraic sum of atomic masses of all the atoms of different elements present in one molecule.
Molecular Mass = average relative mass of one molecule / 1 / 12 th * mass of C-12 atom
[Gram molecular mass or molar mass is molecular mass of a substance expressed in gram.
Molecular mass = 2 * V D ]
Equivalent Mass
It is the mass of an element or a compound which would combine with or displace (by weight) 1 part of hydrogen or 8 parts of oxygen or 35.5 parts of chlorine
Eq. wt. of metal = wt. of metal / wt. of H2displaced * 1.008
= wt. of metal / volume of H2 (in mL) displaced at STP * 11200
Eq. wt. of metal = wt. of metal / wt. of oxygen combined * 8
= wt. of metal / wt. of chlorine combined * 35.5
In general,
Wt. of substance A / Wt. of substance B = Eq. wt. of A / Eq. wt. of B
or for a compound (I) being converted into another compound (II) of same metal
Wt. of compound I / Wt. of compound II
= eq. wt. of metal + eq. wt. of anion of compound I / eq. wt. of metal + eq. wt. of anion of compound II
Eq. mass 0f a salt = formula mass / total positive or negative charge
Equivalent mass = atomic mass or Molecular mass / n factor
n factor for various compounds can be obtained as
(i) n factor for acids i.e., basicity
(Number of ionisable H+ per molecule is the basicity of acid.)
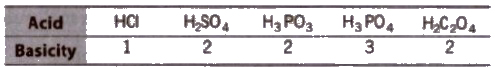
(ii) n factor for bases, i.e., acidity.
(Number of ionisable OH– per molecule is the acidity of a base.)

(iii) In case of ions, 11 factor is equal to charge of that ion.
(iv) In redox titrations, 11 factor is equal to change in oxidation number.

Equivalent mass of organic acid (RCOOH) is calculated by the following formula
Eq. wt. of silver salt of acid (RCOOAg) / Eq. wt. of Ag(or 108) = Vt. of silver salt / Wt. of silver
Stoichiometry
The relative proportions in which the reactants react and the products are formed, is called stoichiometry (from the Greek word meaning ‘to measure an element’.)
Limiting reagent It is the reactant which is completely consumed during the reaction.
Excess reagent It is the reactant which is not completely consumed and remains unreacted during the reaction.
[In a irreversible chemical reaction, the extent of product can be computed on the basis of limiting reagent in the chemical reaction.
Percent Yield
The actual yield of a product in any reaction is usually less than the theoretical yield because of the occurrence of certain side reactions.
Percent yield = actual yield / theoretical yield * 100
Empirical and Molecular Formulae
Empirical formula is the simplest formula of a compound giving simplest whole number ratio of atoms present in one molecule, e.g., CH is empirical formula of benzene (C6H6).
Molecular formula is the actual formula of a compound showing the total number of atoms of constituent elements, e.g., C6H6 is molecular formula of benzene.
Molecular formula = (Empirical formula)n
where, n is simple whole number having values 1, 2, 3, … , etc., and can be calculated as
n = molecular formula mass / empirical formula mass
Follow and Subscribe me for more...😊Thank you
- Get link
- X
- Other Apps

Comments